| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |
| 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 |
| 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 |
| 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 |
| 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 |
- 가치규범의 공공외교
- 주창형 공공외교
- 실버
- 백준 1246번
- Python
- 풀이
- 알고리즘
- 백준 1487번
- 챗봇
- BTREE
- CSS
- 문제 풀이
- N과 M
- 한반도평화와공공외교
- 백준 11050번
- html
- 풍선터뜨리기
- 1141번
- 이항계수
- 해싱
- hashing
- 연산자 문제
- 1
- 해설
- 백준
- DP 알고리즘
- 파이썬
- 백준 14501번
- B-tree
- 0의 개수
- Today
- Total
SunFly의 코딩 및 정보 블로그
B-tree 삽입(insertion) 알고리즘 본문
※ 전체 과정 (삽입될 record가 변수 in_rec에 들어있다고 가정한다.(key값은 in_key에 있다.) )
- 먼저 in_rec를 leaf 노드에 넣고자 시도한다.
- leaf 노드를 탐색하기 위해 B-tree의 루트 노드에서 출발하여 pointer를 따라 leaf 노드에 도달할 때까지 내려간다.
- 도달한 leaf 노드를 Pointer curr 가 가리키게 한다.
- 쌍 <in_rec, P>를 curr가 가리키는 노드 내에 적당한 위치 에 넣어야 한다.
Case 1: curr 노드에 빈 공간이 존재한다
- <in_rec, P>를 적당한 위치에 삽입하고 알고리즘을 종료한다.
Case 2: curr 노드에 빈 공간이 존재하지 않는다.
- Big node(bnode)를 사용한다.
- bnode(정상 node보다 record와 pointer가 하나씩 더 많은 노드)에 <in_rec, P>를 curr노드 안의 rec, pointer와 함께 key값 순서에 맞추어 삽입한다.
- bnode의 center record를 중심으로 left와 right로 나눈다. 이때, left는 curr노드로, right는 새로운 노드(new_node)를 할당하여삽입한다.
- curr의 부모 노드가 존재하는지 탐색한다. (ptr[0]을 이용)
- (1) 만약 curr노드의 부모가 존재한다면 <center record, P>를 넣기 위해 위의 과정을 반복한다.
- (2) curr 노드의 부모가 존재하지 않으면 새로운 루트 노드(new_root_node)를 할당하여 첫 record로 bnode의 center record를 넣는다. ptr[0] -> left node, ptr[1] -> right node가 성립해야한다.

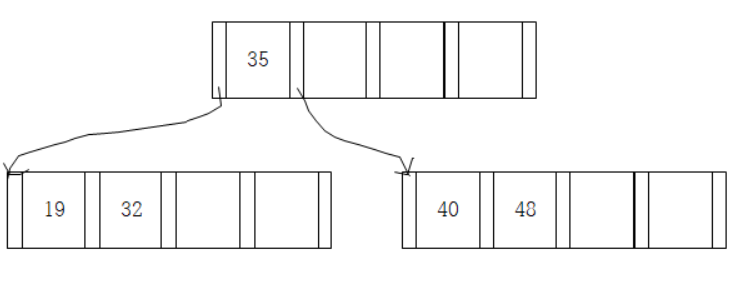
예시) Case2의 경우 : key값이 35인 record를 삽입한다. leaf 노드는 full 상태.


d=2이므로 (2*2/2+ 1)번째 key값 35를 center record라고 하자. 이를 기준으로 왼쪽 19와, 32는 curr노드로, 40과 48은 새로 할당되는 new_node로 삽입된다.
(이때, curr 노드의 parent 노드는 없다고 가정하자.) center record는 새로운 루트노드를 할당하고 그곳에 삽입된다.
★code
// B_tree_Insertion.c
#include "functions.h"
int B_tree_Insertion(nptr_pck package, char CompName[], char from)
{
nodeptr* Root = package->Root;
nodeptr temp_ptr = package->temp_ptr;
nodeptr new_Root = package->new_Root;
nodeptr curr = *Root;
stack stk = NULL;
stack temp_stk = NULL;
stk_pck stk_SET = (stk_pck)malloc(sizeof(stk_pck_rec));
big_node bnode;
bool found = FALSE;
int split_count = 0;
int i = 0;
int k = 0;
stk_SET->stk = &stk;
stk_SET->temp_stk = &temp_stk;
// B-tree가 비어있는 특수한 상황
if (*Root == NULL)
{
*Root = (nodeptr)malloc(sizeof(node));
for (int j = 0; j < PTR_NUM; j++) { //ptr수보다 작을 경우
(*Root)->ptr[j] = NULL;
} // for (j)
strcpy((*Root)->rec[0].name, CompName);
(*Root)->rec[0].leng = strlen(CompName);
(*Root)->fill_cnt = 1;
return split_count;
} // if
// B-tree에 존재 여부 확인
found = leaf_n_del_node_finding(&curr, CompName, stk_SET, 'l');
if (found == TRUE) {
if (from == 'u') {
printf("%s 레코드가 B-tree에 이미 존재합니다.\n", CompName);
} // if ()
return FALSE;
} // if ()
temp_ptr = NULL;
while (1) {
if (curr->fill_cnt < REC_NUM) {
// curr node is not full
for (i = 0; i < curr->fill_cnt; i++) { //fill_cnt 현재 이 노드에 채워져 있는 레코드 수, 넣으려는 값보다 큰 키를 찾는 반복문
if (strcmp(CompName, curr->rec[i].name) < 0) { break; } //strcmp 리턴 값 0보다 크면 첫번째 문자열이 더 큼, 즉 이경우에는 두번째 문자열이 더 큰 경우이다.
} // for (i)
for (int j = curr->fill_cnt; j > i; j--) { //우측으로 한칸씩 shift하여 빈공간을 만드는 반복문.
curr->ptr[j + 1] = curr->ptr[j];
strcpy(curr->rec[j].name, curr->rec[j-1].name);
curr->rec[j].leng = curr->rec[j-1].leng;
} // for (j)
strcpy(curr->rec[i].name, CompName); //빈 공간에 key값 넣기
curr->rec[i].leng = strlen(CompName);
curr->ptr[i + 1] = temp_ptr;
curr->fill_cnt++;
return split_count;
} // if ()
else {
// curr node is full. thus it must be split into two nodes.
if (from == 'u') { split_count++; }
for (i = 0; i < REC_NUM; i++) { //REC_NUM=4, 삽입 공간 탐색
if (strcmp(CompName, curr->rec[i].name) < 0) { break; }
} // for (i)
bnode.ptr[0] = curr->ptr[0];
for (k = 0; k < i; k++) { //삽입 이전
strcpy(bnode.rec[k].name, curr->rec[k].name);
bnode.rec[k].leng = curr->rec[k].leng;
bnode.ptr[k + 1] = curr->ptr[k+1];
} // for (k)
strcpy(bnode.rec[k].name, CompName);
bnode.rec[k].leng = strlen(CompName);
bnode.ptr[k + 1] = temp_ptr; // or curr->ptr[k+1]
k++;
while (i < REC_NUM) { //삽입 이후
strcpy(bnode.rec[k].name, curr->rec[i].name);
bnode.rec[k].leng = curr->rec[i].leng;
bnode.ptr[k + 1] = curr->ptr[i+1];
k++;
i++;
} // while (i)
// move first half of bnode to curr and second half to newly allocated node
for (i = 0; i < CAPACITY_ORDER; i++) {
curr->ptr[i] = bnode.ptr[i];
strcpy(curr->rec[i].name, bnode.rec[i].name);
curr->rec[i].leng = bnode.rec[i].leng;
} // for (i)
curr->ptr[i] = bnode.ptr[i];
// [CAPACITY_ORDER]번째 이상 정리
for (int l = CAPACITY_ORDER; l < REC_NUM; l++) { //curr의 빈공간을 전부 NULL로 초기화
strcpy(curr->rec[l].name, "");
curr->rec[l].leng = 0;
curr->ptr[l + 1] = NULL;
} // for (l)
curr->fill_cnt = CAPACITY_ORDER;
temp_ptr = (nodeptr)malloc(sizeof(node));
for (i = 0; i < CAPACITY_ORDER; i++) {
temp_ptr->ptr[i] = bnode.ptr[CAPACITY_ORDER + i + 1];
strcpy(temp_ptr->rec[i].name, bnode.rec[CAPACITY_ORDER + i + 1].name);
temp_ptr->rec[i].leng = bnode.rec[CAPACITY_ORDER + i + 1].leng;
} // for (i)
temp_ptr->ptr[i] = bnode.ptr[CAPACITY_ORDER + i + 1];
for (int m = CAPACITY_ORDER + 1; m < PTR_NUM; m++) {
temp_ptr->ptr[m] = NULL; //Split한 뒤를 NULL 초기화
} // for (m)
temp_ptr->fill_cnt = CAPACITY_ORDER; //SPlit한 뒤 fill_cnt = 2
strcpy(CompName, bnode.rec[CAPACITY_ORDER].name); //가운데 값을 CompName에 넣고 변경함.
if (stk) { stk_pop(&stk, &curr); }
else {
// curr은 root와 같다.
// 새로운 root node를 만든다.
new_Root = (nodeptr)malloc(sizeof(node));
new_Root->ptr[0] = curr;
new_Root->ptr[1] = temp_ptr;
for (int j = 2; j < PTR_NUM; j++) {
new_Root->ptr[j] = NULL;
} // for (j)
strcpy(new_Root->rec[0].name, CompName);
new_Root->rec[0].leng = strlen(CompName);
new_Root->fill_cnt = 1;
*Root = (new_Root);
return split_count;
} // else
} // else
} // while (1)
}
'알고리즘' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 이진 탐색 트리(Binary Search Tree)란? (0) | 2021.10.11 |
|---|---|
| B-tree 구현 (C언어 구현) (0) | 2021.10.11 |
| B-tree 삭제(Deletion) 알고리즘 (Redistribution/Merge 알고리즘) (0) | 2021.10.11 |
| B-tree 탐색(searching or Retrieval) 알고리즘 (0) | 2021.10.11 |
| B-tree 알고리즘이란? (0) | 2021.10.10 |



